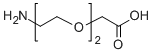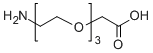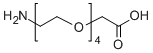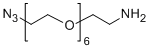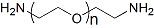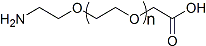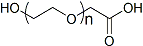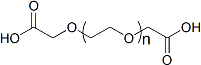PEG多肽化学修饰介绍
多肽是由多个氨基酸通过肽键连接而成的化合物。它们在生物体中普遍存在。迄今为止,已在生物体中发现了数千种多肽。多肽在生命活动中对各系统、器官、组织、细胞的功能活动发挥着重要的调节作用。常用于功能分析、抗体研究、药物开发等领域。随着生物技术和多肽合成技术的成熟,越来越多的多肽药物被开发并应用于临床。
多肽修饰有很多种,简单分为后修饰和过程修饰(利用衍生氨基酸)。根据修饰位点的不同,有N端修饰、C端修饰、侧链修饰、氨基酸修饰、骨架修饰等。作为改变肽链主链结构或侧链基团的重要手段、肽修饰可以有效改变肽化合物的理化性质,增加水溶性,延长在体内的作用时间,改变其生物分布,消除免疫原性,减少毒副作用等。这里主要介绍几种主要的肽修饰策略和特点。
1.环化
环肽在生物医学方面有很多应用,许多具有生物活性的天然肽都是环肽。由于环肽比线性肽刚性更强,因此对消化系统具有很强的抵抗力,能在消化道中存活,并且与目标受体有更强的亲和力。环化是合成环状多肽最直接的方法,特别是对于结构骨架较大的多肽。按环化方式可分为侧链-侧链型、末端-侧链型、末端-末端型。
(1) 侧链到侧链
最常见的侧链-侧链环化类型是半胱氨酸残基之间的二硫键。最常见的侧链-侧链环化类型是半胱氨酸残基之间的二硫键桥接。引入环化方法是通过将一对半胱氨酸残基脱保护,然后氧化形成二硫键。它可以选择性地除去巯基保护基团,从而实现形成多个环。环化可以在解离后在溶剂中进行,也可以在解离前在树脂上进行。由于树脂上的肽不易形成环化构象,因此树脂上的环化可能比溶剂中的环化效率低。
另一种类型的侧链-侧链环化是在天冬氨酸或谷氨酸残基与碱性氨基酸之间形成酰胺结构。它要求多肽的侧链保护无论是在树脂上还是解离后的碱基都必须能够选择性去除。第三种侧链-侧链环化是通过酪氨酸或对羟基苯基甘氨酸形成二苯醚。天然产物中的这种环化仅存在于微生物产物中,环化产物往往具有潜在的药用价值。这些化合物的制备需要的反应条件,因此它们不常用于常规多肽的合成。
(2) 终端到侧链
末端侧链环化通常涉及C末端和赖氨酸或鸟氨酸侧链的氨基,或者N末端和天冬氨酸或谷氨酸侧链。还有一些多肽环化是通过末端C与丝氨酸或苏氨酸侧链之间形成醚键来实现的。
(3)端对端或头对尾
链状多肽可以在溶剂中环化或通过侧链环化固定在树脂上。在溶剂中环化应使用低浓度的多肽以避免多肽的寡聚化。头尾相连合成的环肽的产量取决于链肽的序列。因此,在大规模制备环肽之前,应首先创建可能的链状先导肽文库,然后进行环化,寻找能够达到最佳结果的序列。
2.N-甲基化
N-甲基化首先出现在天然肽中,并被引入肽合成中以阻止氢键的形成,从而使肽更能抵抗生物降解和清除。利用N-甲基化氨基酸衍生物合成肽是最重要的方法。此外,N-(2-硝基苯磺酰氯)肽-树脂中间体也可用于与甲醇的Mitsunobu反应。该方法已用于制备含有N-甲基化氨基酸的环肽文库。
3.磷酸化
磷酸化是自然界最常见的翻译后修饰之一。在人体细胞中,超过30%的蛋白质被磷酸化。磷酸化,特别是可逆磷酸化,在许多细胞过程的控制中发挥着重要作用,例如信号转导、基因表达、细胞周期和细胞骨架调节以及细胞凋亡。
可以在各种氨基酸残基上观察到磷酸化,但最常见的磷酸化目标是丝氨酸、苏氨酸和酪氨酸残基。磷酸酪氨酸、磷酸苏氨酸和磷酸丝氨酸衍生物可以在合成期间引入到多肽中或者可以在多肽合成之后形成。选择性磷酸化可以通过使用可以选择性去除保护基的丝氨酸、苏氨酸和酪氨酸残基来实现。一些磷酸化试剂也可以进行后修饰以将磷酸基团引入多肽中。近年来,有学者利用化学选择性施陶丁格-亚磷酸酯反应实现赖氨酸的位点特异性磷酸化。
4.肉豆蔻酰化和棕榈酰化
N 末端被脂肪酸酰化使得肽或蛋白质能够与细胞膜结合。 N端的肉豆蔻酰化序列可以靶向Src家族的蛋白激酶和逆转录酶Gaq蛋白,从而与细胞膜结合。可以使用标准偶联反应将肉豆蔻酸连接到树脂-多肽的N末端,并且可以在标准条件下解离所得脂肽并通过RP-HPLC纯化。
5.糖基化
万古霉素和替考拉宁等糖肽是治疗耐药细菌感染的重要抗生素,其他糖肽也常用于刺激免疫系统。此外,由于许多微生物抗原都被糖基化,因此糖肽的研究对于提高感染的治疗效果具有重要意义。另一方面,一些研究发现肿瘤细胞细胞膜上的蛋白质表现出异常的糖基化,这使得糖肽在癌症和肿瘤免疫防御研究中也发挥着重要作用。糖肽的制备一般采用Fmoc/t-Bu法。糖基化残基,如苏氨酸和丝氨酸,通常通过五氟苯酚酯活化的 Fmoc 保护的糖基化氨基酸引入多肽中。
6.异戊二烯化
异戊二烯化发生在靠近C末端的侧链上的半胱氨酸残基处。蛋白质的异戊二烯化可以增加细胞膜的亲和力,形成蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用。异戊烯化蛋白包括酪氨酸磷酸酶、小 GTP 酶、共伴侣分子、核纤层和着丝粒结合蛋白。异戊二烯化的多肽可以通过在树脂上异戊二烯化或通过引入半胱氨酸衍生物来制备。
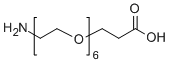
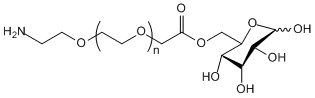
7.聚乙二醇(PEG)改性
PEG 修饰可用于改善蛋白水解稳定性、生物分布和肽溶解度。在多肽上引入PEG链可以改善其药理性质,还可以抑制蛋白水解酶对多肽的水解。 PEG多肽比普通多肽更容易通过肾小球毛细血管横截面,大大降低肾脏清除率。
由于PEG多肽在体内的有效半衰期延长,因此可以通过使用较低剂量和较低频率的多肽药物来维持正常的治疗水平。但PEG修饰也有负面影响。大量的PEG会阻止酶降解多肽,但也会减少多肽与靶受体的结合。然而,PEG多肽的低亲和力通常被其较长的药代动力学半衰期所抵消。通过在体内停留更长时间,PEG 多肽更有可能被靶组织吸收。因此,应优化 PEG 聚合物的规格以获得最佳结果。另一方面,由于肾脏清除率降低,PEG多肽可在肝脏中积聚并引起大分子综合征。所以,当肽用于药物测试时,需要更仔细地设计 PEG 修饰。
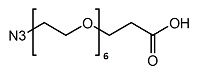
PEG修饰剂常见的修饰基团可概括如下:氨基(-Amine)-NH2、氨甲基-CH2-NH2、羟基-OH、羧基-COOH、硫氢基(-Thiol)-SH、马来酰亚胺-MAL、琥珀酰亚胺碳酸酯- SC、琥珀酰亚胺乙酸酯-SCM、琥珀酰亚胺丙酸酯-SPA、N-羟基琥珀酰亚胺-NHS、丙酸基-CH2CH2COOH、醛基-CHO(如丙醛-ALD、丁醛-butyrALD)、丙烯酸(-Acrylate)-ACRL、叠氮基-叠氮化物、生物素-生物素、荧光素-荧光素、戊二酸-GA、酰肼-酰肼、炔基-炔、对甲苯磺酸盐-OTs、琥珀酰亚胺基琥珀酸盐-SS等。带有羧酸的PEG衍生物可以与N-偶联。末端胺或赖氨酸侧链。氨基活化的 PEG 可以与天冬氨酸或谷氨酸侧链偶联。MAL激活的PEG可以与全脱保护的半胱氨酸侧链的硫醇偶联[11]。 PEG修饰剂的常见分类如下(注:mPEG为甲氧基-PEG、CH3O-(CH2CH2O)n-CH2CH2-OH):
(1)线性PEG修饰剂
mPEG-SC、mPEG-SCM、mPEG-SPA、mPEG-OTs、mPEG-SH、mPEG-ALD、mPEG-丁醇 ALD、mPEG-SS
(2)双功能PEG修饰剂
HCOO-PEG-COOH、NH2-PEG-NH2、OH-PEG-COOH、OH-PEG-NH2、HCl·NH2-PEG-COOH、MAL-PEG-NHS
( 3)支链PEG修饰剂
(mPEG)2-NHS、(mPEG)2-ALD、(mPEG)2-NH2、(mPEG)2-MA7
8.生物素化
生物素可以与亲和素或链霉亲和素强烈结合,结合强度甚至接近共价键。生物素标记的肽通常用于免疫测定、组织细胞化学和基于荧光的流式细胞术。标记的抗生物素抗体也可用于结合生物素化的多肽。生物素标签通常附着在赖氨酸的侧链或 N 末端。通常使用 6-氨基己酸作为肽和生物素之间的连接物。该链接可以灵活地与基底结合,并且在空间位阻下可以更好地结合。
9.荧光标记
荧光标记可用于追踪活细胞中的肽,以及研究酶和作用机制。色氨酸 (Trp) 具有荧光性,因此可用于内部标记。色氨酸的发射光谱取决于周围环境,并随着溶剂极性的降低而降低。该特性对于检测肽结构和受体结合非常有用。色氨酸荧光可以被质子化的天冬氨酸和谷氨酸猝灭,这可能限制其使用。丹磺酰氯基团(Dansyl)与氨基结合时具有高荧光性,也常用于氨基酸或蛋白质的荧光标记。
荧光共振能量转换(FRET)对于酶研究非常有用。当使用FRET时,底物肽通常含有荧光标记基团和荧光猝灭基团。标记的荧光团将通过非光子能量转移被猝灭剂猝灭。当肽与所研究的酶解离时,标记基团会发出荧光。
10.包层肽
笼形多肽具有光学可去除的保护基团,可以屏蔽多肽与受体的结合。当受到紫外线照射时,肽将被激活,恢复其与受体的亲和力。由于这种光学激活可以根据时间、幅度或位置进行控制,因此包合物多肽可用于研究细胞中发生的反应。笼形多肽常用的保护基是2-硝基苄基及其衍生物,可以在多肽合成过程中通过受保护的氨基酸衍生物引入。已开发的氨基酸衍生物包括赖氨酸、半胱氨酸、丝氨酸和酪氨酸。然而,天冬氨酸和谷氨酸衍生物并不常用,因为它们在肽合成和解离过程中容易环化。
11.多聚体抗原肽(MAP)
短肽通常不具有免疫性,必须与载体蛋白偶联才能产生抗体。多聚抗原肽(MAP)由多个相同的多肽连接到赖氨酸核心上组成,可以特异性表达高效免疫原,可用于制备肽-载体蛋白偶联物。 MAP多肽可以通过在MAP树脂上固相合成来逐步合成。然而,不全的偶联会导致某些分支上的肽链缺失或截断,从而无法显示原始MAP多肽的特性。作为替代方法,可以单独制备和纯化多肽,然后将其偶联至MAP。连接到肽核心的肽序列清晰,可以通过质谱轻松表征。
结论
肽修饰是设计肽的重要方法。化学修饰的肽不仅可以保持较高的生物活性,而且可以有效避免免疫原性和毒性的缺点。同时,化学修饰可以赋予肽一些新的优异性能。 。近年来,利用CH活化的方式对肽进行后期修饰的方法也得到迅速发展,并取得了许多重要成果。